문제 링크 : programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/17676
코딩테스트 연습 - [1차] 추석 트래픽
입력: [ "2016-09-15 20:59:57.421 0.351s", "2016-09-15 20:59:58.233 1.181s", "2016-09-15 20:59:58.299 0.8s", "2016-09-15 20:59:58.688 1.041s", "2016-09-15 20:59:59.591 1.412s", "2016-09-15 21:00:00.464 1.466s", "2016-09-15 21:00:00.741 1.581s", "2016-09-1
programmers.co.kr
문제 유형
구현, Sweeping
문제 자체는 [백준]1689_겹치는 선분 과 비슷하다.
위 문제처럼 각 구간의 시작점에 1, 끝점에 -1의 가중치를 둔 후 좌표의 오름차순으로 훑으며
가중치 합의 최댓값을 찾는 방식으로 접근할 수 있지만, 이 문제는 조금 다르게 접근해야 한다.
이 문제에서 요구하는 정답이 특정 시각을 기준으로 1초 길이의 구간 내에 들어오는 요청의 최대 개수를 묻기 때문이다.
즉, 겹치는 선분 문제에서는 다음과 같은 정답을 요구했다면,

이 문제는 다음과 같은 정답을 요구하기 때문이다.
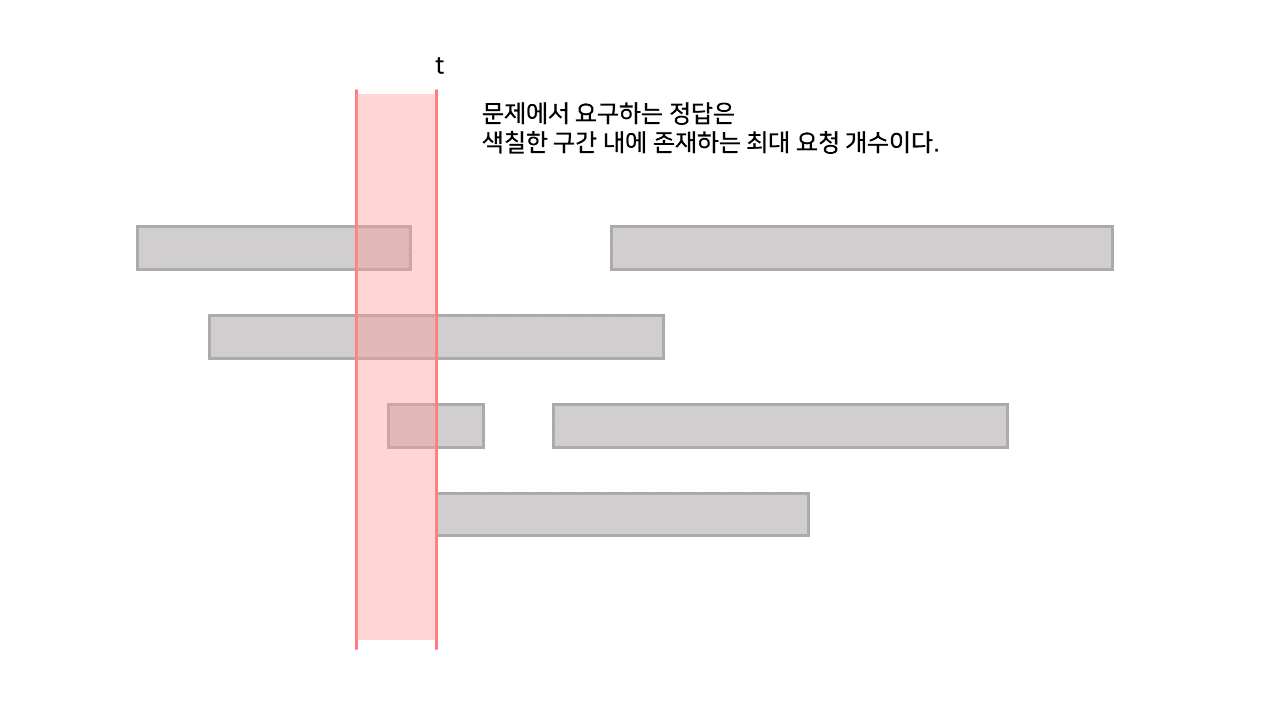
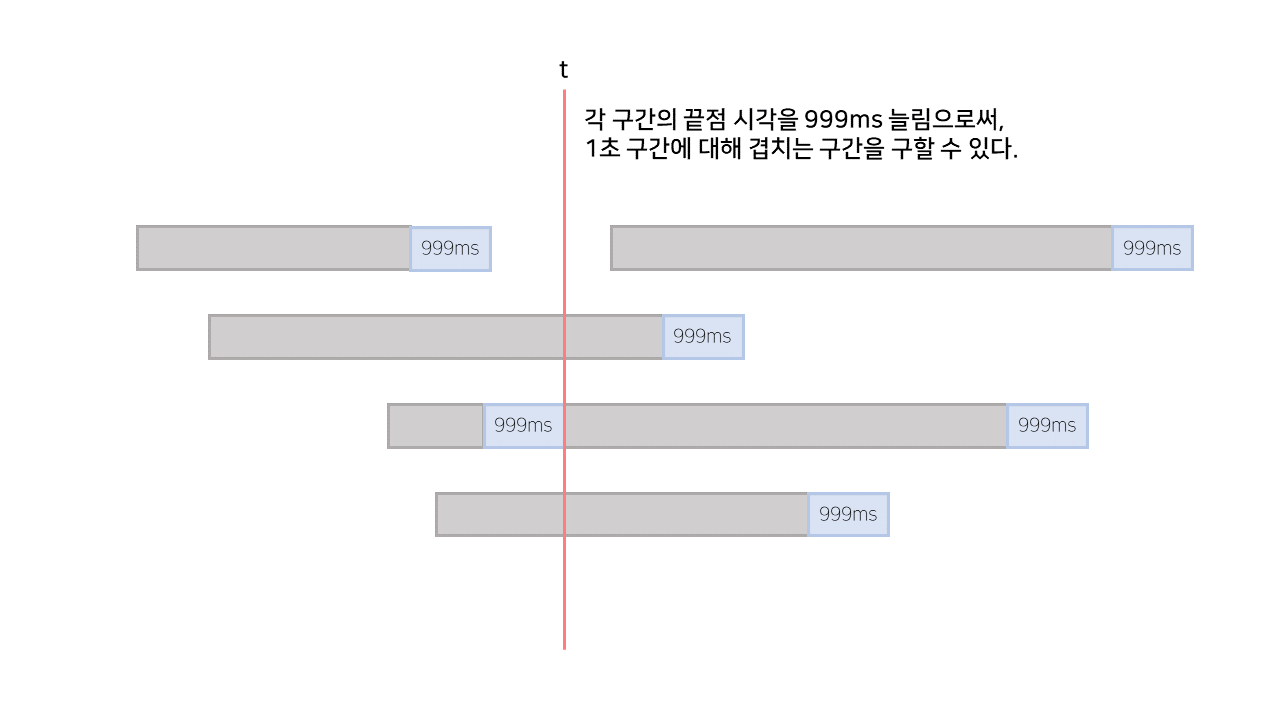
따라서, 문제를 다음과 같이 바꿔준다면 겹치는 선분 문제와 동일한 해법으로 해결할 수 있다.
[코드]
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> p;
vector<p> points;
int sweeping(){
int ret = 0, cnt = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++){
cnt += points[i].second;
ret = max(ret, cnt);
}
return ret;
}
int get_len(string timestr){
//x.xxx 형태로 들어옴
int s = atoi(timestr.substr(0, 1).c_str());
int ms = 0, div = 100;
for(int i = 2; i < timestr.size(); i++){
if(timestr[i] == 's') break;
ms += (timestr[i] - '0') * div;
div /= 10;
}
return s * 1000 + ms;
}
void process(string timestr, int len){
int h = atoi(timestr.substr(0, 2).c_str());
int m = atoi(timestr.substr(3, 2).c_str());
int s = atoi(timestr.substr(6, 2).c_str());
int ms = atoi(timestr.substr(9, 3).c_str());
int basetime = (h * 3600 + m * 60 + s) * 1000 + ms;
points.push_back({basetime + 999, -1});
points.push_back({basetime - len + 1, 1});
}
bool compare(p a, p b){
if(a.first == b.first) return a.second > b.second; //끝점이 포함이므로
return a.first < b.first;
}
int solution(vector<string> lines) {
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++)
process(lines[i].substr(11, 12), get_len(lines[i].substr(24)));
sort(points.begin(), points.end(), compare);
answer = sweeping();
return answer;
}
|
cs |
스위핑 자체의 시간복잡도는 O(N)이 된다.
'알고리즘 > 프로그래머스 문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [프로그래머스] 뉴스 클러스터링 (0) | 2021.03.08 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스] 외벽 점검 (1) | 2021.02.17 |
| [프로그래머스] 자물쇠와 열쇠 (0) | 2021.02.17 |
| [프로그래머스] 매출 하락 최소화 (0) | 2021.02.14 |
| [프로그래머스] 카드 짝 맞추기 (0) | 2021.02.14 |